Overview
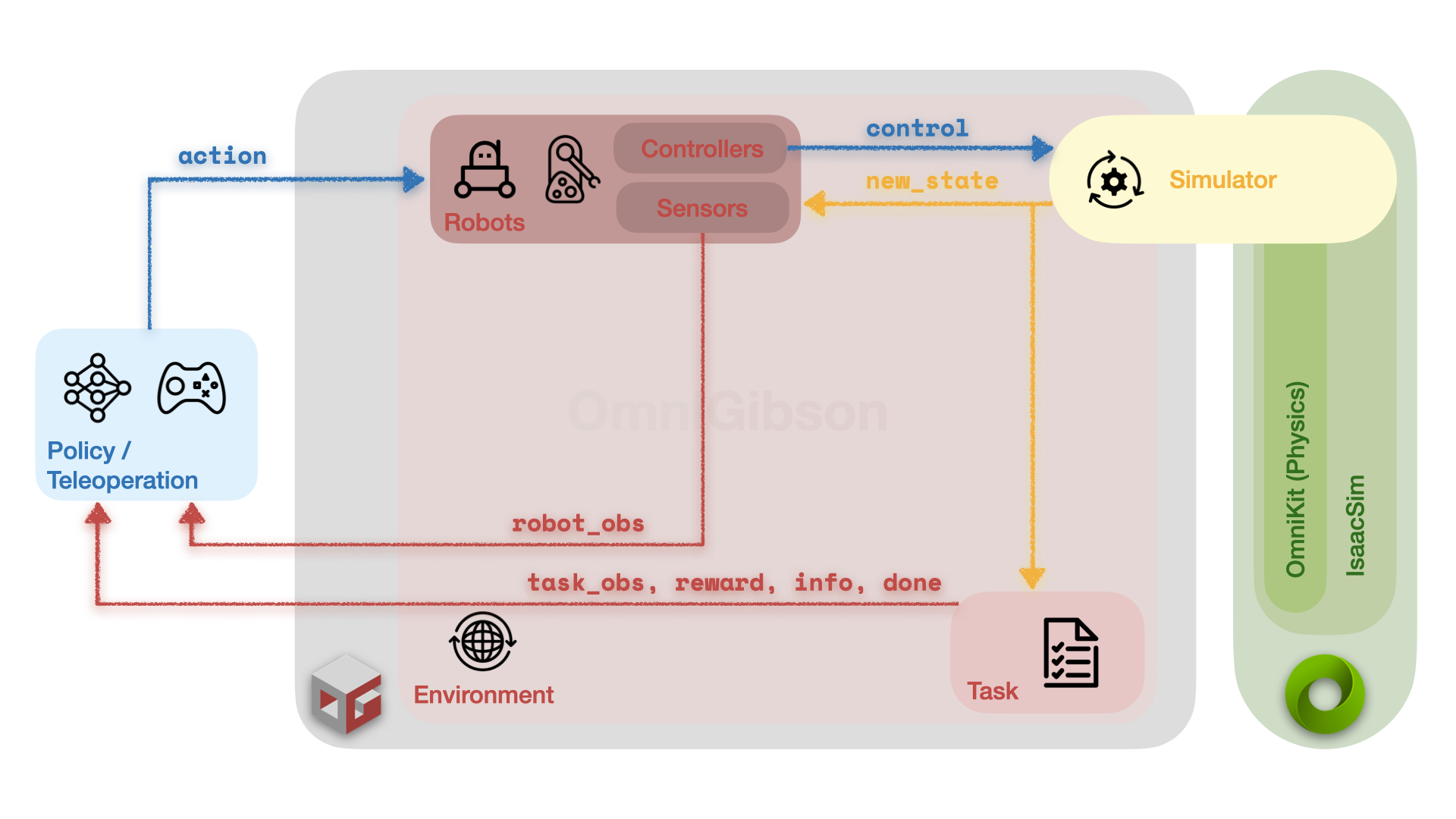
OmniGibson's framework provides modular APIs for (a) quickly interacting with different components of a created environment and (b) prototyping and developing custom environments.
OmniGibson is built upon NVIDIA's IsaacSim, a powerful simulation platform that uses PhysX as the physics backend.
We build upon IsaacSim's Simulator interface to construct our Environment class, which is an OpenAI gym-compatible interface and the main entry point into OmniGibson. An Environment instance generally consists of the following:
- A
Sceneinstance, which by default is a "dummy" (empty) or a full-populated (InteractiveTraversableScene) instance, - A
BaseTaskinstance, which can range from a complexBehaviorTask, navigationPointNavigationTask, or no-opDummyTask, - Optionally, one or more
BaseRobots, which define the action space for the given environment instance, - Optionally, one or more additional
BaseObjects, which are additional object models not explicitly defined in the environment's scene
The above figure describes OmniGibson's simulation loop:
- Action Execution: An externally defined
actionis passed toRobotinstances in theEnvironment, which is processed by each robot's own set ofControllers and converted into low-level joint commands that are then deployed on the robot. - Simulation Stepping: The simulator takes at least one (and potentially multiple) physics steps, updating its internal state.
- Observation Retrieval: Sensors on each
Robotinstance grab observations from the updated simulator state, and the loadedTaskinstance also computes its task-relevant observations and updates its internal state. The observations as well as task-relevant data is then returned from theEnvironmentinstance.
Each of the modules in OmniGibson can be extended by the user, and allow for custom subclass implementations to be used without needing to directly modify OmniGibson source code. This section provides high-level overviews of each of the modules, as well as general insight into the purpose and intended use-cases of each module.